Pancakes and waffles have long been staples of breakfast menus across the globe, loved for their comforting taste and versatility. Yet, in recent years, culinary enthusiasts and home cooks alike have taken these traditional dishes to new heights by incorporating creative twists—whether through innovative ingredients, presentation techniques, or flavor pairings. This article explores how creative pancakes and waffles are transforming breakfast culture, offering both visual appeal and unique taste experiences. We will examine practical examples, nutritional variations, and emerging trends shaping the future of these beloved breakfast icons.
Reimagining the Basic: From Traditional to Trendy
Pancakes and waffles originated as simple batter-based dishes, frequently served with butter and syrup. For instance, classic American pancakes use a basic combination of flour, eggs, milk, and baking powder. Waffles share a similar base but rely on a specific iron pattern to achieve their signature crispy texture. However, the contemporary culinary landscape challenges these basic formulas.
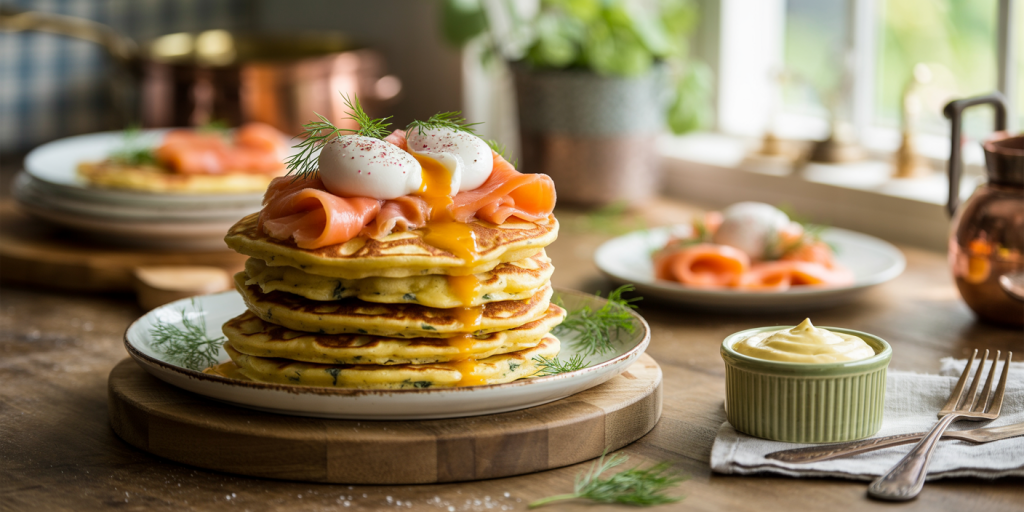
One notable example is the rise of savory pancakes and waffles. Chefs in casual and fine dining settings are experimenting with incorporating ingredients such as cheese, herbs, and vegetables directly into the batter. In Portland, Oregon, a restaurant called *Egg and Flour* offers their famed Cheddar and Chive Waffles, which pair wonderfully with smoked ham and poached eggs. Making these variations involves tweaking traditional recipes to balance moisture and flavor, ensuring that the final product remains both fluffy and crisp.

Beyond savory innovations, there is also a surge in incorporating global flavors. Matcha pancakes from Japan and spiced cardamom waffles from India have gained popularity in international brunch menus. For example, a matcha pancake recipe will include powdered green tea, offering a vibrant color and a subtle earthy taste, enriched with antioxidants. Such creative fusions not only diversify flavor profiles but also imbue pancakes and waffles with cultural significance, broadening their appeal.

Nutritional Enhancements Through Creative Ingredients
Health-conscious consumers increasingly demand breakfast options that deliver nutrition alongside flavor. Pancakes and waffles, traditionally rich in carbohydrates and sugars, are being reinvented with healthier twists that do not compromise taste or texture.
One effective strategy is replacing refined flour with whole grain alternatives such as oat flour, buckwheat, or almond flour. Buckwheat, for instance, is gluten-free and high in fiber and minerals, making buckwheat pancakes favorable for diabetic and gluten-sensitive individuals. According to a 2020 study published in the *Journal of Food Science and Technology*, substituting wheat flour with buckwheat flour improved the nutritional profile and increased antioxidant activity in pancakes without negatively affecting consumer acceptance.
Additionally, enriching batters with protein sources such as Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, or plant-based alternatives (e.g., pea protein powder) has gained traction. A New York-based breakfast café called *Protein Plate* offers protein-packed waffles made with egg whites and pea protein, targeting fitness enthusiasts. The appeal lies in supporting muscle synthesis and satiety while delivering a familiar breakfast experience.
To accommodate various dietary needs, vegan and gluten-free pancakes and waffles are widely available. Aquafaba (chickpea water) can substitute eggs to provide binding power, while gluten-free flours (like rice or chickpea flours) maintain texture. These adaptations expand accessibility, proving that creativity in recipes can bridge taste and health seamlessly.
| Ingredient Variation | Nutritional Benefit | Common Use Case | Example Dish |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buckwheat flour | Gluten-free, high fiber | Diabetic-friendly pancakes | Buckwheat and blueberry pancakes |
| Greek yogurt | High protein, probiotics | Protein-enhanced waffles | Yogurt waffle with fresh fruit |
| Aquafaba | Egg substitute, vegan | Vegan pancakes | Vegan chocolate chip pancakes |
| Almond flour | Low-carb, rich in vitamin E | Gluten-free, keto waffles | Almond flour waffles with berries |
Creative Presentation and Toppings: Elevating Visual Appeal
Beyond taste, presentation plays a crucial role in the evolving pancake and waffle scene, especially in social media-driven cultures. Creative plating and topping combinations contribute to a multisensory experience.
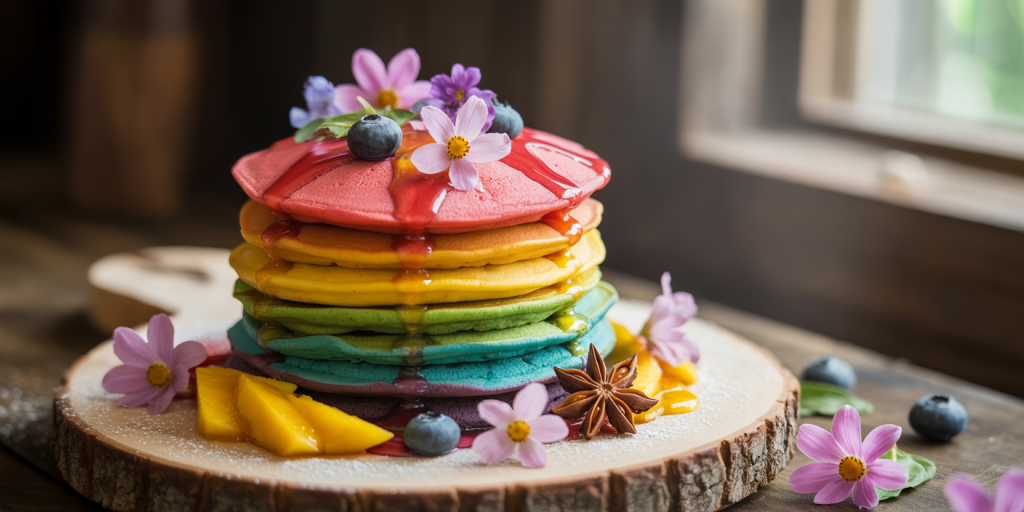
For example, *Rainbow Pancakes* have swept visual platforms like Instagram, where multiple layers of brightly colored batters are stacked to create a vibrant, eye-catching dish. These pancakes are typically made by dividing batter into separate bowls, adding natural food coloring, and cooking each color independently before assembling. In San Francisco’s trendy café *Hue Pancake House*, rainbow pancakes remain a top seller, capitalizing on novelty and aesthetics.

Toppings have also diversified dramatically. Classic maple syrup and butter are now often accompanied or replaced by exotic alternatives such as yuzu syrup, hibiscus glaze, or matcha-infused honey. Additionally, homemade compotes, candied nuts, edible flowers, and whipped mascarpone add complexity to the flavor and appearance. Waffle cones filled with fresh fruit and cream are another popular innovation, merging dessert functionality with breakfast tradition.
The trend of layering flavor and texture contrasts simultaneously—crispness from nuts or toasted granola, creaminess from custards or mascarpone, and bursts of acidity from fruit gels—has been effectively employed in boutique brunch venues worldwide. This emphasis on texture and creativity encourages customers to see pancakes and waffles as more than just food but as artful experiences.
Global Inspirations Shaping Creative Pancakes and Waffles
The globalization of food culture has led to intriguing cross-cultural adaptations of pancakes and waffles. From the Chinese scallion pancake to the Dutch stroopwafel, these international variants offer exciting templates for creative reinterpretation.
In South Korea, *Hotteok*—a filled pancake with sugar and nuts—is being reimagined in fusion restaurants. Some chefs add cream cheese and savory fillings, making them appealing to different palates. Similarly, Belgian waffles, known for their deep grid texture, now find themselves customized with ingredients such as speculoos spread or dark chocolate ganache, designed to marry traditional flavors with contemporary tastes.
This global influence fosters an appreciation of pancakes and waffles as adaptable canvases. Fusing ingredients from distinct culinary heritages can lead to unique, compelling dishes. For example, a fusion café in London creatively blends Japanese matcha batter with French crepe-style waffles, topped with fresh berries and azuki bean paste. Such hybrid forms celebrate culinary diversity and innovation.
A comparative look at global styles underscores these variations:
| Style | Origin | Key Ingredients | Typical Serving Style | Typical Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Pancakes | USA | All-purpose flour, eggs, milk | Stacked with syrup and butter | Sweet, fluffy, mild |
| Hotteok | South Korea | Wheat flour, brown sugar, nuts | Filled, pan-fried | Sweet, chewy, nutty |
| Stroopwafel | Netherlands | Wheat flour, caramel syrup | Thin waffle cookies sandwiched with syrup | Sweet, caramel-rich |
| Matcha Pancakes | Japan | All-purpose flour, matcha | Layered with fresh cream or fruit | Earthy, mildly sweet |
Practical Tips for Home Cooks: Making Creativity Accessible
While some creative pancakes and waffles require specialty ingredients or stove-side expertise, many variations are accessible to home cooks seeking to elevate their breakfast routine.
Firstly, starting with a standard recipe and experimenting by adding mix-ins—such as mashed banana, shredded coconut, or chopped nuts—can drastically change the flavor profile. For example, adding mashed ripe banana to pancake batter increases sweetness and moisture, reducing the need for added sugars. It also boosts potassium intake, which supports cardiovascular health.
Secondly, creative toppings do not require culinary mastery. Combining standard elements like Greek yogurt, honey, and fresh berries can provide both nutritional benefits and a sophisticated appearance. For waffles, serving with a dollop of ricotta and sliced figs can impress guests with minimal effort.
For those willing to explore international flavors, purchasing supplementary ingredients like matcha powder, tahini, or cardamom can unlock a world of new possibilities. Using natural food colorings from beetroot powder or turmeric can achieve vibrant presentations without artificial additives.
The following quick recipe example illustrates a creative savory waffle variation suitable for home preparation:
Savoury Herb and Cheese Waffles: Basic waffle batter base Add 1/4 cup shredded cheddar cheese Mix in 1 tablespoon chopped fresh herbs (thyme, chives, parsley) Cook in waffle iron, serve topped with smoked salmon and a dollop of sour cream or crème fraîche
This simple adjustment complements the traditional waffle’s flavor with a savory dimension that works well for brunch or light lunches.
Future Perspectives: Trends in Pancakes & Waffles
Looking ahead, the world of creative pancakes and waffles is poised for continued expansion driven by evolving dietary preferences, technology, and cultural exchange.
One anticipated trend is increased incorporation of functional ingredients—like adaptogenic herbs (ashwagandha, maca), superfoods (spirulina, chia seeds), and probiotics (fermented batters)—to enhance health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Industry reports suggest that consumer interest in wellness-compatible foods is rising by 7% annually, with breakfast meals being particularly scrutinized for both nutritional integrity and convenience (Source: Mintel Global Food and Drink Trends 2023).
Technological advances such as smart waffle irons with customizable settings are making precise cooking easier, allowing home cooks to achieve professional results. Similarly, 3D food printing could enable novel pancake shapes, textures, and embedded flavors, potentially revolutionizing presentation.
Environmental sustainability is also influencing ingredient sourcing. Plant-based flours derived from alternative crops (e.g., sorghum, millet) and locally sourced fresh toppings reduce carbon footprints and meet consumers’ ecological values.
Finally, experiential dining—where customers participate in creating or customizing pancake and waffle dishes—is growing. Interactive brunch spots that allow patrons to select batters, mix-ins, and toppings at the table are becoming viral sensations.
In summary, pancakes and waffles are no longer confined to simple comfort foods. Creativity in recipes, nutrition, presentation, and cultural fusion is transforming them into dynamic, multifaceted meals suited to modern tastes and values.