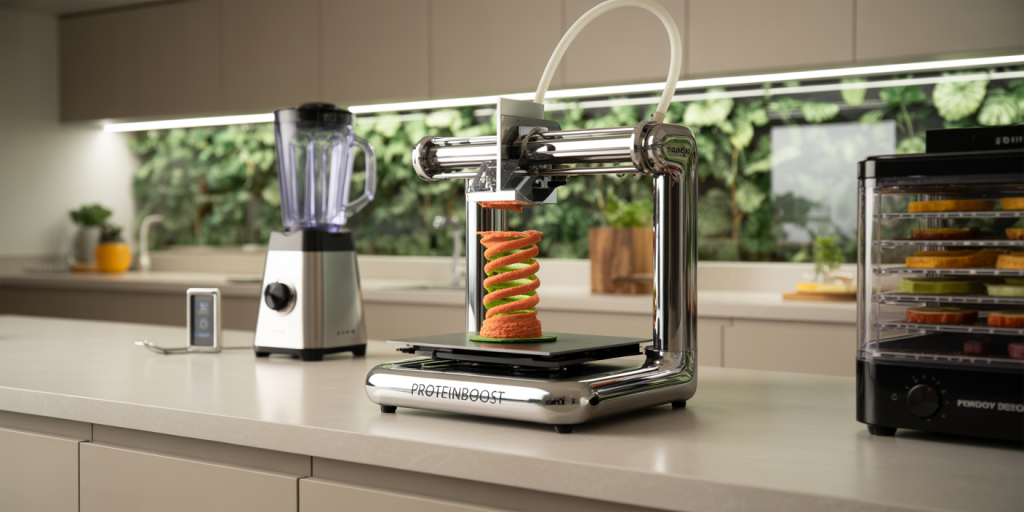
Breakfast is often regarded as the most important meal of the day. What people choose to eat in the morning varies greatly around the globe, influenced by cultural, climatic, and economic factors. This diversity in breakfast choices reflects deep-rooted traditions, nutritional needs, and local food availability. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into global eating habits and promote healthier, balanced diets worldwide.
Morning meals serve a crucial role in replenishing glycogen stores, providing energy, and setting the tone for the day’s productivity. According to a study by the International Food Information Council (IFIC) in 2023, approximately 64% of adults worldwide eat breakfast daily, though what they consume differs significantly depending on the region. Let’s explore some signature breakfast styles from around the world, their nutritional impact, and what the future holds for this essential meal.
Traditional European Breakfasts: From Hearty to Simple
European breakfasts vary widely between northern and southern countries but generally reflect the cultural preference for either hearty or light starts to the day. In Northern Europe, for instance, breakfast tends to be substantial and protein-focused.
In countries like Germany and Sweden, breakfasts often include cold cuts, cheese, boiled eggs, and dense whole-grain breads. The emphasis on proteins and fibers aims to provide long-lasting energy throughout the morning. For example, a typical Swedish “frukost” may consist of rye bread topped with cheese and cucumber slices alongside eggs and coffee. This combination supports satiety and stable blood sugar levels, as demonstrated in a 2022 nutritional study published in the *European Journal of Clinical Nutrition* indicating that higher protein intake at breakfast reduces mid-morning hunger.
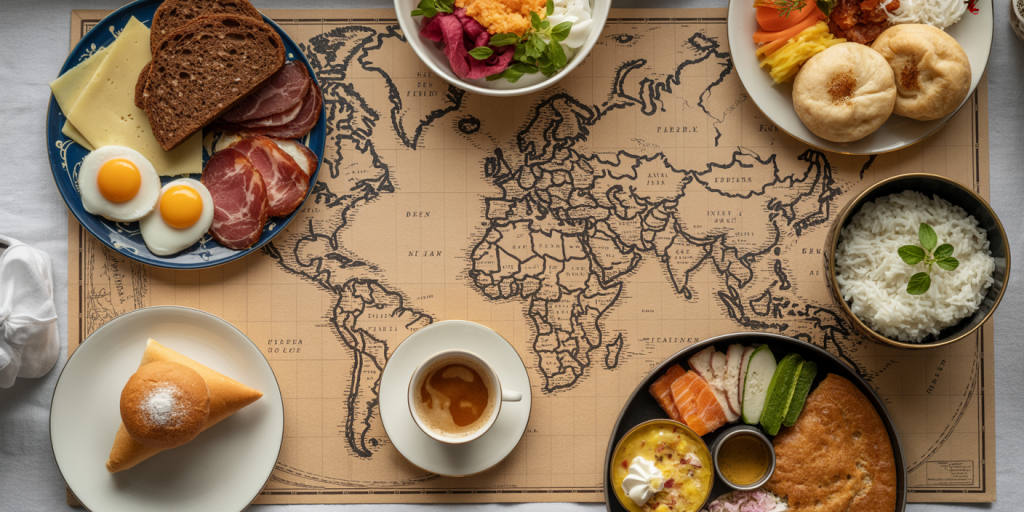

Conversely, Southern European countries like Italy and Spain favor lighter breakfasts such as espresso paired with pastries. The classic Italian breakfast often includes a cornetto, a flaky, sweet croissant similar to the French version. While these meals are lower in protein and fiber, the Mediterranean diet traditionally compensates with nutrient-rich lunches and dinners. Research from the Mediterranean Diet Foundation (2021) highlights that individuals from these regions maintain excellent cardiovascular health despite lighter morning meals, largely attributed to overall diet quality.
Asian Breakfast Traditions: A Blend of Nutrition and Flavor
Asia’s vast geography and cultural heterogeneity produce some of the most diverse breakfast customs worldwide. Many Asian breakfasts balance carbohydrates, proteins, and vegetables, resulting in nutritionally complete meals.
In Japan, traditional breakfasts include steamed rice, miso soup, grilled fish, and pickled vegetables. This combination offers complex carbohydrates, probiotics, lean protein, and fiber all at once. A real-world example is the Japanese “asa gohan,” consumed commonly across households and hotels. Studies by the Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science (2022) suggest that this balanced approach promotes stable energy release and supports gut health, contributing to Japan’s high longevity rates.
Similarly, in India, breakfast varies by region. Northern India might feature parathas (stuffed flatbreads) with yogurt and pickles, while southern India favors idlis (steamed rice cakes) and sambar (lentil-based vegetable stew). These meals provide a blend of complex carbs, plant-based proteins, and micronutrients. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), traditional Indian breakfasts assist in maintaining blood sugar regulation even in populations at risk of type 2 diabetes when prepared with whole grains and minimal oil.
Breakfast in the Americas: From Sweet to Savory
The Americas highlight an eclectic mix of breakfast types, often blending indigenous, European, and modern influences. The US and Canada, for example, tend toward either quick convenience foods or hearty meals depending on lifestyle.
A typical North American breakfast could range from cereals and toast to bacon, eggs, and pancakes. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES, 2023) show that many Americans consume higher calorie breakfasts, often rich in sugars and fats, which may contribute to metabolic issues. However, awareness about healthier options is rising, with a growing market for protein-rich and low-sugar products.
In contrast, Latin American countries often emphasize savory components at breakfast. In Mexico, a traditional breakfast might include chilaquiles — fried tortilla pieces simmered in salsa, topped with eggs and cheese — offering a high-energy start suitable for physically active populations. Meanwhile, in Brazil, pão de queijo (cheese bread) and fresh fruit are common. Both meals focus on providing sufficient carbohydrates and protein. Nutrition experts like the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) advocate for maintaining traditional breakfasts with fresh ingredients rather than shifting to processed alternatives to prevent rising obesity rates in the region.
| Region | Typical Breakfast Items | Nutritional Highlights | Cultural Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Europe | Whole-grain bread, cold cuts, cheese, boiled eggs | High protein, fiber | Hearty, energy-sustaining meals |
| Southern Europe | Espresso, pastries (cornetto, croissants) | Lower protein, higher carbs and sugars | Lighter meals, Mediterranean diet |
| Japan | Rice, miso soup, grilled fish, pickles | Balanced macros, probiotics | Longevity-linked diet habits |
| India | Parathas, idlis, sambar, yogurt | Complex carbs, plant protein, fiber | Regional diversity, diabetic-friendly |
| North America | Cereals, pancakes, bacon, eggs | Higher calories, sugars, fats | Convenience and variety |
| Latin America | Chilaquiles, pão de queijo, eggs, fresh fruit | Balanced carbs and proteins | Traditional, fresh ingredients |
The Impact of Breakfast on Health: Nutritional Insights
Beyond cultural alliances, breakfast’s nutritional role has garnered scientific interest globally. Data from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023) establishes a correlation between consistent breakfast consumption and improved cognitive function, weight management, and metabolic health. Skipping breakfast has been linked to increased risks for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Nutritionally balanced breakfasts support glucose metabolism and satiety hormones, reducing unhealthy snacking later in the day. For example, a protein-rich breakfast can reduce daily caloric intake by up to 15%, according to a randomized control trial involving 400 participants in Australia (Nutrition Reviews, 2022). This has implications for public health strategies, especially in countering obesity and metabolic syndromes.
Practical case studies highlight successful initiatives to improve breakfast quality in school systems. In Finland, introducing cooked, nutrient-dense breakfasts in schools resulted in enhanced academic performance and reduced absenteeism (Finnish National Board of Education, 2021). This underscores the importance of breakfast not only for individual health but also for societal well-being.
Breakfast Preferences Among Younger Generations
As globalization and urban lifestyles evolve, breakfast habits among younger generations are also changing. Millennials and Gen Z consumers demonstrate a preference for convenience as well as health consciousness.
Ready-to-eat breakfasts such as smoothies, protein bars, oatmeals, and cold-pressed juices have surged in popularity worldwide. Market reports by Mintel (2023) indicate that 38% of consumers aged 18-34 in the US and Europe opt for grab-and-go nutritious options rather than traditional cooked breakfasts. This shift reflects modern time constraints but also an increased demand for functional foods enriched with vitamins, minerals, and adaptogens.
Social media trends also influence breakfast choices. For example, the “overnight oats” phenomenon showcases a healthy, quick-to-prepare meal with customizable ingredients catering to diverse nutritional needs and taste preferences. Conversely, some regions observe a decline in traditional breakfasts, raising concerns about the loss of cultural culinary practices.

Future Perspectives: The Evolution of Breakfast Trends
Looking ahead, breakfast around the world is poised to evolve in response to health, environmental, and technological factors. Sustainable eating is becoming a significant consideration, encouraging the incorporation of plant-based ingredients to reduce carbon footprints. The rise of plant-based milks, vegan pastries, and alternative proteins such as pulses and mycoproteins is evident in breakfast products globally.
Technological advances in food production, like 3D-printed foods and personalized nutrition apps, also promise to revolutionize breakfast habits. AI-driven dietary recommendations tailored to individual metabolic profiles could optimize morning meals for better health outcomes.
Moreover, public health policies are increasingly recognizing breakfast as a critical element in tackling nutrition-related diseases. Campaigns promoting nutrient-rich breakfasts and reducing sugar intake in school meals are being implemented in countries such as the UK and Australia. Such initiatives aim to preserve cultural uniqueness while adapting to contemporary nutritional science.
There is also growing interest in intermittent fasting patterns as an alternative to the traditional breakfast routine. While some studies suggest skipping breakfast might offer benefits in specific contexts, experts generally agree that a balanced, nutrient-dense morning meal remains optimal for most populations.
Ultimately, breakfast’s future reflects a balance between honoring diverse traditions and embracing scientific innovation to improve global health.