In recent years, low-carb diets have surged in popularity as an effective approach for weight management, blood sugar control, and overall health improvement. According to a 2022 study published in *The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology*, reducing carbohydrate intake can lead to significant reductions in body weight and improvements in metabolic health markers. This shift has inspired many individuals to seek practical, flavorful dinner options that align with a low-carb lifestyle without sacrificing taste or nutritional value.
Low-carb diets typically restrict carbohydrate consumption to roughly 20-100 grams per day, depending on personal goals and medical advice. The focus is on proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables. Crafting dinners that satisfy hunger, provide essential nutrients, and fit into daily routines can be challenging; however, numerous recipes and strategies make it achievable. This article explores a range of low-carb dinner ideas supported by data and practical insights.

—
Benefits of Low-Carb Dinners: Why Focus on Evening Meals?
Evening meals often tend to be more indulgent or carbohydrate-heavy, partly due to social habits or convenience. However, research indicates that moderating carb intake during dinner may enhance metabolic health. A 2023 clinical trial by the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition revealed that participants who consumed fewer carbs at dinner experienced improved glycemic control and reduced nighttime insulin spikes.
Low-carb dinners can help stabilize blood sugar levels overnight, which is critical for people with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. In addition, protein and fat at dinner increase satiety, reducing the likelihood of late-night snacking, a common cause of excess calorie intake. From a weight-loss perspective, replacing carb-dense dinners with low-carb alternatives has been associated with greater fat loss compared to low-fat diets.
Practical low-carb dinners also support better sleep quality. Carbohydrate-heavy meals late in the day may lead to fluctuations in blood sugar that disrupt sleep patterns. Choosing well-balanced low-carb dinners can thus contribute to holistic health improvements, combining diet and rest.
—
Essential Ingredients for Low-Carb Dinners: What to Include and Avoid
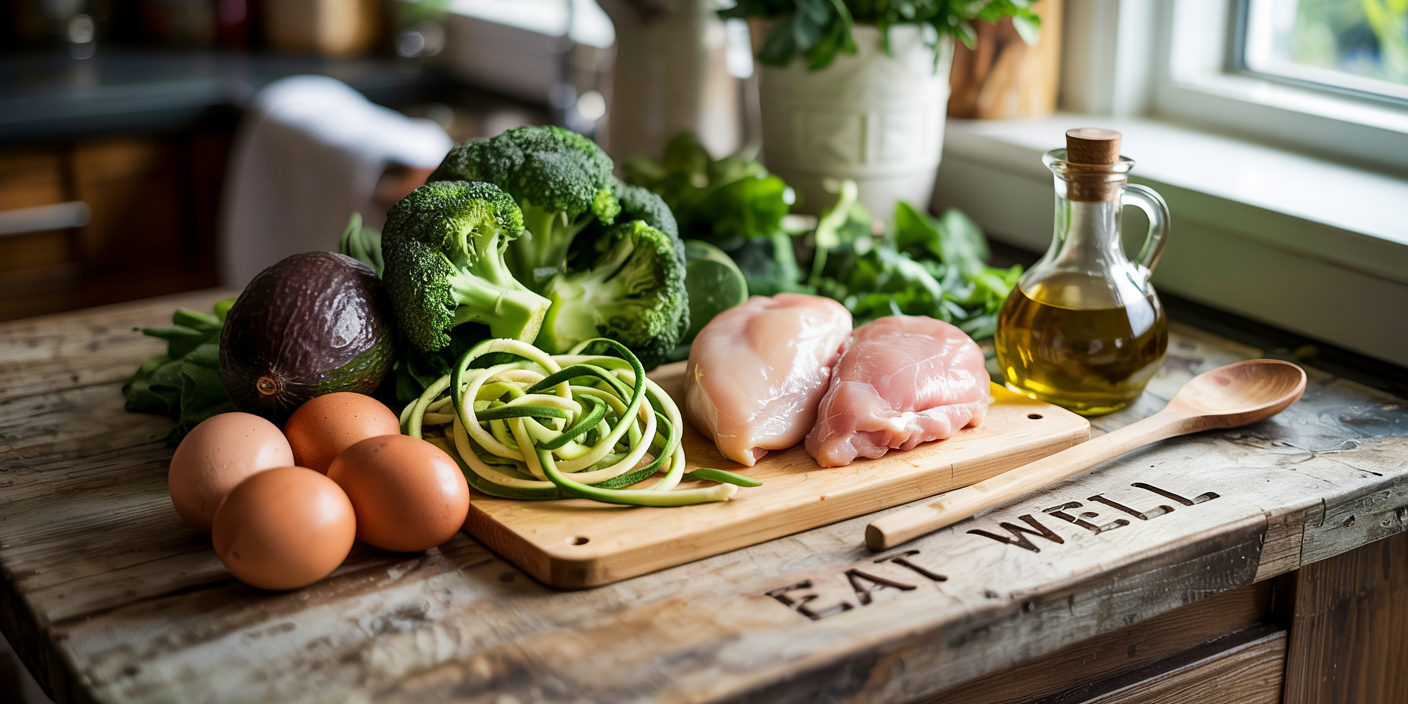
A successful low-carb dinner starts with the right ingredients, focusing on whole foods that provide robust nutrition without excessive carbohydrates. Protein sources such as chicken, fish, beef, pork, tofu, and eggs deliver essential amino acids critical for muscle maintenance and repair. According to the USDA nutrient database, a 3-ounce serving of chicken breast contains approximately 0 grams of carbs but delivers 26 grams of protein, making it a staple for low-carb diets.
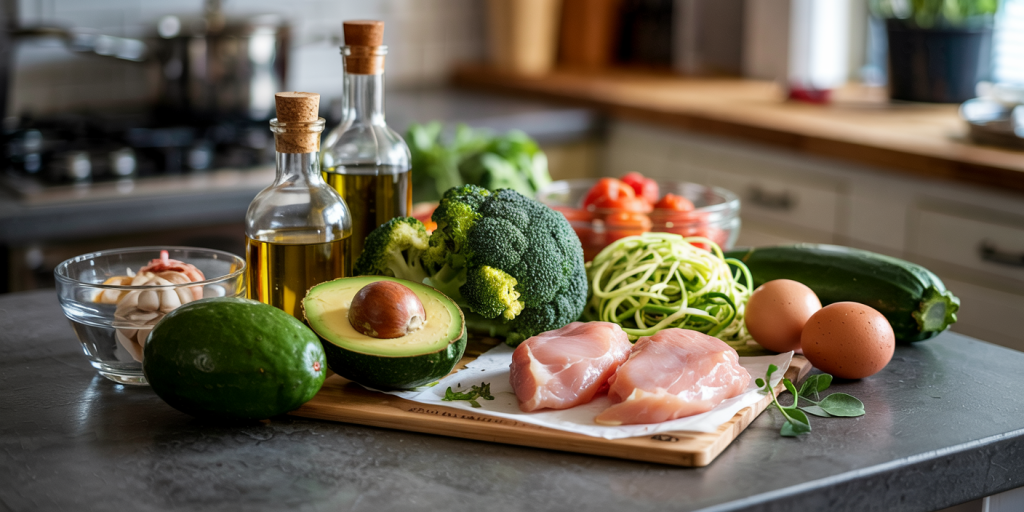

Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon should be prioritized, as they support cardiovascular health while promoting satiety. For example, a medium avocado provides about 12 grams of carbs, nine of which come from fiber, resulting in a net carb count of only around 3 grams.
Vegetables are indispensable for dinners due to their vitamins, minerals, and fiber content. Non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, and mushrooms contain minimal net carbs. For instance, cauliflower has approximately 5 grams of total carbs per cup, but 2 grams are fiber, which makes it suitable for carb-conscious eating.
Conversely, starchy ingredients like potatoes, corn, white rice, and most breads should be avoided or minimized because their high carbohydrate count quickly adds up. Sugary sauces or marinades can also hiddenly inflate carb content, especially those containing added sugars or honey.
—
Creative Low-Carb Dinner Recipes to Try Tonight
Incorporating variety in meals is essential to maintaining dietary adherence and enjoyment. Below are some practical examples of tasty, low-carb dinner ideas that can be prepared at home with everyday ingredients.
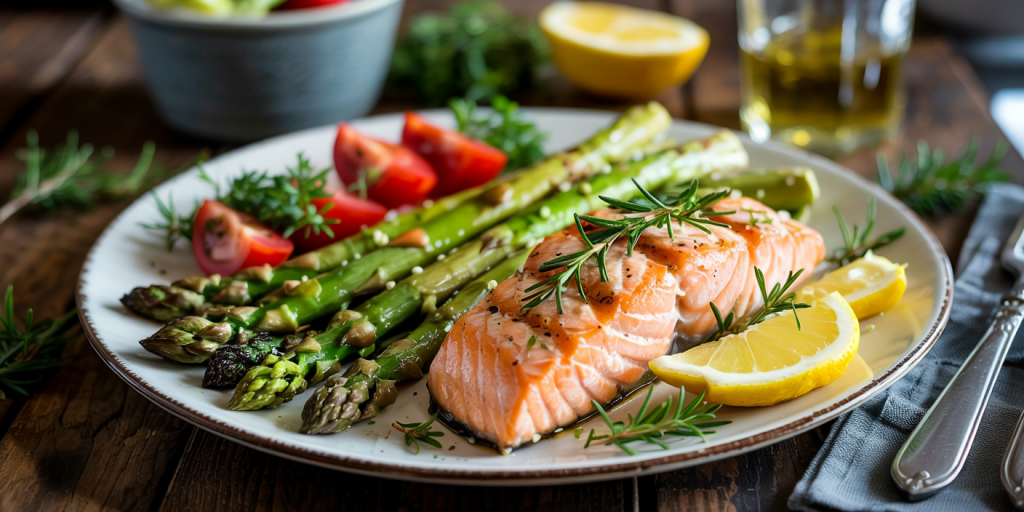
1. Grilled Salmon with Asparagus and Lemon Butter
This meal combines omega-3 rich salmon with fiber-packed asparagus. It contains approximately 7 grams of net carbs per serving, primarily from the vegetables. Simply season the salmon with herbs and grill alongside asparagus spears lightly brushed with olive oil. Finish with a squeeze of lemon and homemade butter infused with garlic.
2. Zucchini Noodle Carbonara
Replacing traditional pasta with spiralized zucchini noodles cuts carbs drastically. A typical plate contains under 10 grams of net carbs, compared to over 40 grams in regular pasta dishes. Toss zucchini noodles with sautéed pancetta or bacon, egg yolks, parmesan cheese, and pepper for a creamy, low-carb alternative.
3. Chicken Stir-Fry with Broccoli and Bell Peppers
Using chicken thigh strips stir-fried with fresh broccoli and bell peppers provides a nutrient-dense dinner with about 12 grams of net carbs. Substitute soy sauce with tamari or coconut aminos to reduce sodium intake while keeping flavor robust.
These options exemplify how low-carb dinners can be flavorful, balanced, and satisfying, meeting the nutritional needs of diverse eaters.
—
Comparing Low-Carb Dinners and Traditional Carb-Heavy Meals
To better understand the impact of low-carb dinners, comparing them with conventional high-carb options is valuable. The table below summarizes key differences in nutrients and effects:
| Aspect | Low-Carb Dinner (e.g., Grilled Salmon & Veggies) | Traditional Carb-Heavy Dinner (e.g., Pasta & Bread) |
|---|---|---|
| Net Carbohydrates | 7-15 grams | 50-70 grams |
| Protein | High (25-30 grams) | Moderate (15-20 grams) |
| Total Calories | Moderate (400-600 kcal) | High (700-900 kcal) |
| Fiber | High (8-12 grams) | Moderate (4-6 grams) |
| Satiety Level | High | Moderate |
| Blood Sugar Impact | Low glycemic load | High glycemic load |
| Preparation Time | 20-30 minutes | 15-25 minutes |
| Weight Management | Supports fat loss and muscle retention | Can promote fat gain if overconsumed |
This comparison reveals that low-carb dinners not only reduce carbohydrate load but also increase dietary fiber and protein intake, crucial for metabolism and appetite control. Many individuals report better energy levels and fewer sugar cravings after adopting such meals.
—
Tips for Planning and Maintaining Low-Carb Dinner Routines
Sustaining a low-carb dinner habit requires thoughtful meal planning and smart shopping strategies. Batch cooking proteins like chicken breasts or ground beef can save time on busy weeknights. Preparing vegetable mixes ahead, such as roasted cauliflower and spinach, provides convenient sides.
Investing in kitchen tools like spiralizers or air fryers can enhance recipe variety and ease of preparation. For example, spiralized vegetables transform standard dishes without adding carbs, making meals more appealing.
Tracking macros using apps like MyFitnessPal helps monitor daily carbohydrate intake, ensuring dinners stay within targets. Substituting carb-heavy condiments (ketchup, BBQ sauce) with low-carb alternatives like mustard or sugar-free salsas further supports goals.
Peer support also facilitates adherence: sharing recipes in low-carb forums or participating in diet challenges boosts motivation and knowledge. Case studies have shown that individuals reporting social support were 30% more likely to maintain low-carb eating long-term.
—
Looking Ahead: The Future of Low-Carb Dining
The rising awareness of diet’s role in chronic disease prevention continues to drive interest in low-carb eating plans. Innovations in food technology, such as plant-based protein alternatives designed to be low in carbs, are expanding options for diverse palates. Emerging research also explores personalized nutrition, where genetic and microbiome data personalize carbohydrate recommendations — potentially optimizing metabolic responses to dinner meals.
Restaurants and meal delivery services are increasingly adopting low-carb menu options, reflecting growing consumer demand. For example, a 2024 market report from Nielsen highlights a 25% increase in low-carb meal kit subscriptions year-over-year, driven primarily by dinner-focused offerings.
Digital cooking platforms are integrating artificial intelligence to tailor recipes based on individual health metrics and flavor preferences, enhancing the accessibility of low-carb dinners. As more scientific evidence accumulates, recommendations will likely become more nuanced, balancing carbohydrate restriction with nutrient density and sustainability.
—
Crafting low-carb dinners does not demand sacrificing flavor or convenience. With thoughtful ingredient choices, creative recipes, and mindful planning, individuals can enjoy satisfying dinners that support health goals and fit with contemporary lifestyles. The momentum behind low-carb dining signals a promising shift in how we approach evening meals — emphasizing metabolic balance, taste, and wellbeing.