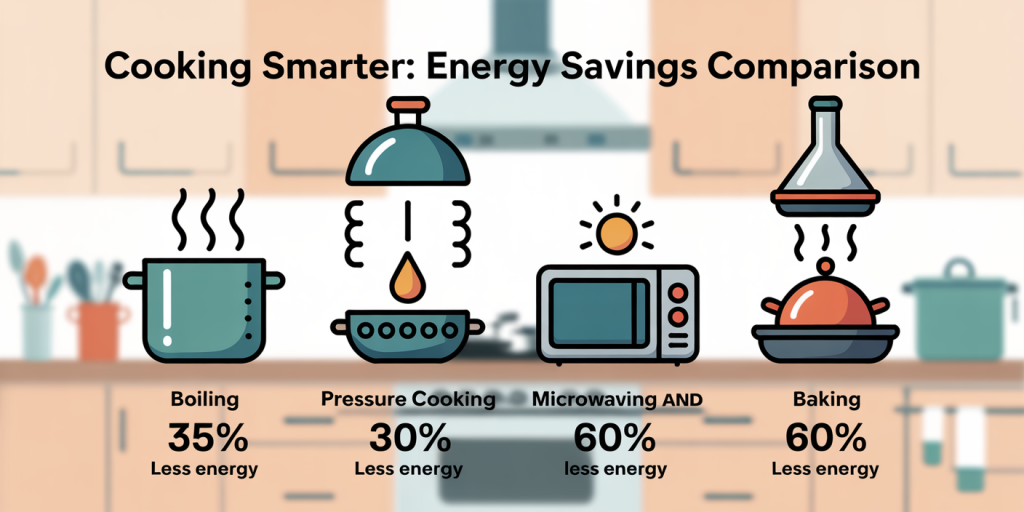
Maintaining a well-organized refrigerator is essential for reducing food waste, optimizing storage space, and ensuring your groceries stay fresh longer. According to the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), the average American family wastes approximately 25% of the food they buy, much of which spoils in improperly stored conditions. A thoughtfully organized fridge not only saves money but also contributes to a healthier lifestyle and more sustainable living.
In this article, we explore practical tips and strategies for fridge organization—leveraging appliance zones, storage innovations, and lifestyle habits to transform your refrigerator into a model of efficiency. Whether you have a compact apartment fridge or a large professional-grade model, these insights will help you make the most of your cold storage space.
—
Understanding Fridge Zones: Optimize Storage by Temperature and Humidity
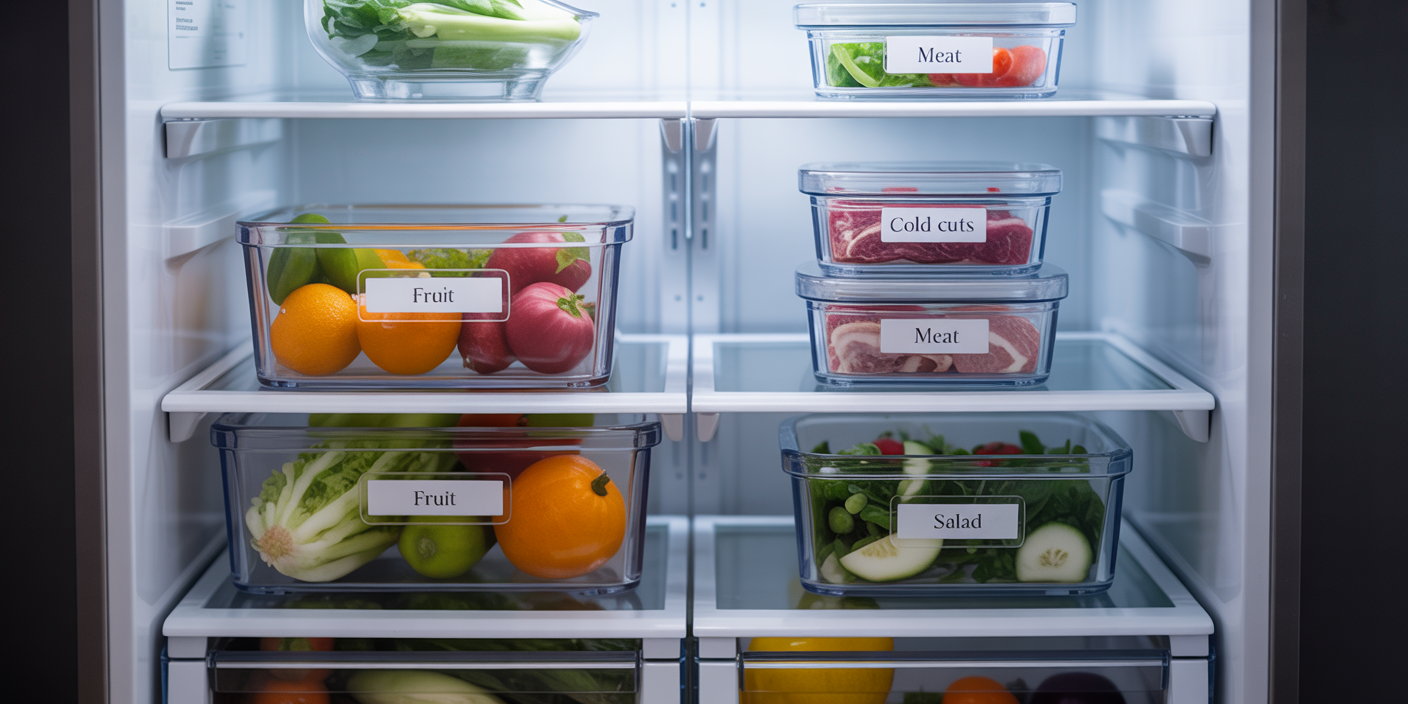
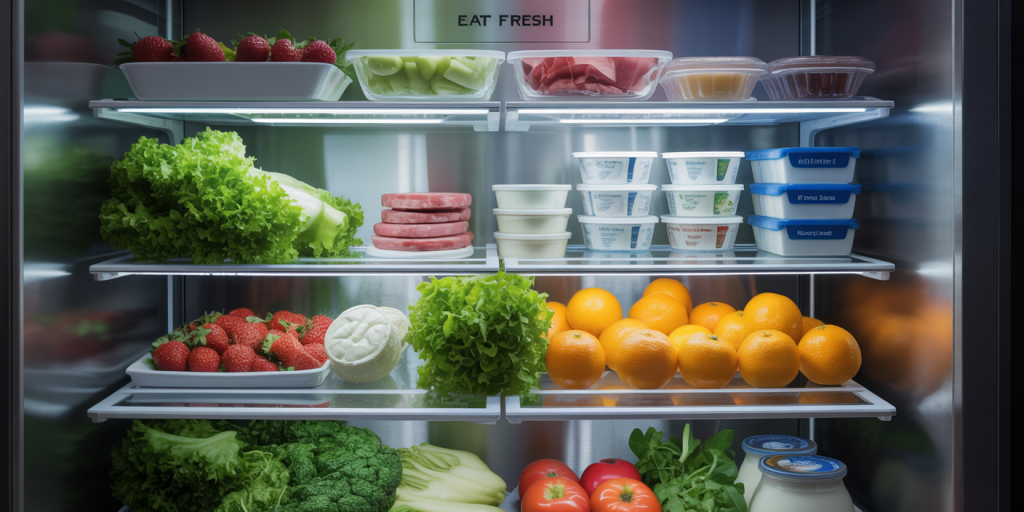
Every refrigerator has different storage zones that maintain varying temperatures and humidity levels. Properly categorizing where items should go will help preserve freshness and prevent food spoilage.
The crisper drawers, for example, generally maintain the highest humidity levels, ideal for storing fruits and vegetables. Vegetables such as leafy greens and broccoli thrive in high humidity environments, while fruits typically prefer slightly lower humidity to slow down moisture-related decay. Many modern fridges come with humidity controls on their crisper drawers to fine-tune this balance.
The upper shelves typically have a more consistent, moderate temperature, suitable for dairy products like cheese and yogurt. Meanwhile, the cooler parts at the back of the bottom shelves are best for meat and seafood, as these items require the lowest temperatures, ideally between 32°F (0°C) and 40°F (4°C) to inhibit bacterial growth. It’s advisable to keep raw meats in leak-proof containers to prevent cross-contamination.
Zone Temperature Guide and Ideal Foods Storage
| Fridge Zone | Temperature Range (°F) | Suitable Food Items |
|---|---|---|
| Top Shelf | 36-40 | Leftovers, drinks, dairy products |
| Middle Shelf | 36-38 | Eggs, cooked meats, ready-to-eat foods |
| Bottom Shelf | 32-36 | Raw meat, poultry, fish (in sealed containers) |
| Crisper Drawers | 32-40 (humidity controlled) | Vegetables (high humidity), fruits (low humidity) |
| Door Compartments | 40-45 | Condiments, juices, water bottles |
This zoning method minimizes spoilage and maintains the quality of diverse food types, giving your fridge a systematic flow.

—
Decluttering and Categorizing: Habits to Maintain an Organized Fridge
A cluttered fridge can lead to forgotten items, expired products, and inefficiencies in food preparation. A fundamental step in fridge organization is decluttering—regularly checking expiry dates, discarding spoiled items, and removing duplicates or excess stock.
One practical approach is to categorize foods into groups such as dairy, meats, vegetables, fruits, condiments, and leftovers. Using clear storage bins or baskets fosters visibility and neatness by corraling similar items together. For example, all cheeses can be stored in a stackable container with ventilation holes to maintain optimal moisture balance, while leftovers can be consolidated in uniform, stackable glass or BPA-free plastic containers labeled with dates.
In a case study conducted in 2023 by the Consumer Reports organization, households that invested in clear bins and refrigerators with adjustable shelving experienced a 30% reduction in food waste over six months. This underscores the efficiency benefits of systematic categorization.
Regularly cleaning your fridge every 1–2 weeks ensures that no spills or residue cause cross-contamination or odors, further enhancing food safety and cleanliness.
—
Smart Labeling and Rotation Techniques to Preserve Freshness
Effective labeling and stock rotation methods significantly boost fridge efficiency. The “First In, First Out” (FIFO) principle, widely used in retail and food service, applies equally in household fridges. By placing newer items behind older ones and marking opened products with the date of opening, you can prioritize consumption and reduce spoilage.
Writable magnetic chalk labels or dry-erase markers on the bins allow quick updates without damaging storage containers. Digital smartphone apps, such as “Fridge Pal” or “Fresh Box,” facilitate tracking of expiration dates and inventory management, making the process more straightforward and tech-savvy.
For example, Marie, a working mother from Chicago, shared how this labeling method helped her reduce the expiration-related waste of dairy and produce by nearly 40% in three months, saving her an estimated $25 monthly on groceries.
By habitually rotating stock and noting purchase dates visibly, you nurture a disciplined consumption pattern that avoids buying duplicates and tossing out expired food.
—
Utilizing Specialized Storage Containers for Maximum Efficiency
The type of container you use for food storage affects space utilization and shelf life. Airtight containers, vacuum-sealed bags, and reusable silicone storage options can significantly extend freshness and keep your fridge organized.

Vegetables stored in perforated bags or vented containers last longer by balancing moisture and airflow. For instance, studies show that lettuce stored in vented containers maintains crispness 2-3 days longer than those wrapped in cling film.
For meat and fish, vacuum sealing removes excess air, impeding oxidation and bacterial growth. A 2022 research report by the Journal of Food Preservation found vacuum-packaging extended refrigerated beef shelf life by up to 40% compared to traditional wrapping.
Stackable modular containers optimize vertical space, crucial for narrow or shallow refrigerators. Matching container sizes with fridge compartments prevents wasted gaps, while clear containers allow easy visibility of contents, reducing retrieval time and accidental spoilage.
—
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Through Organized Refrigeration
A well-organized refrigerator not only preserves food quality but also contributes to lowering energy consumption—a critical factor given that refrigeration accounts for approximately 14% of residential electricity use in the U.S., according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Clutter reduces proper air circulation inside the fridge, forcing the compressor to run longer to maintain temperatures. When items block venting or airflow paths, temperatures fluctuate and lead to energy waste. Organized zoning and avoiding over-stuffing the fridge keeps cold air circulating freely and optimizes appliance performance.
Additionally, storing food in appropriately sized containers and cleaning coils regularly enhances efficiency. Modern refrigerators with temperature-controlled drawers and LED lighting also consume less energy as they allow targeted cooling and minimize heat emission.

By saving energy and reducing food waste simultaneously, consumers can lower their carbon footprint. The EPA estimates that food waste contributes up to 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making responsible refrigeration practices a small yet meaningful action toward environmental sustainability.
—
Future Trends in Fridge Organization: Smart Technology and AI Integration
Looking forward, refrigerator design and organization are poised to evolve rapidly with the integration of smart technology and artificial intelligence (AI). Some high-end models are already equipped with internal cameras that track inventory, alert users when items are nearing expiration, and even suggest recipes based on available ingredients.
Future smart fridges are expected to include automated temperature zoning that dynamically adjusts humidity and cooling depending on food types detected by sensors. AI-driven apps will analyze consumption patterns and recommend shopping lists, minimizing over-purchasing and waste.
Imagine a fridge that orders groceries for you when staples run low or sends notifications to your mobile device if the door remains open accidentally—features that enhance convenience while maintaining food safety.
In addition to technology, more sustainable materials and modular designs that allow better customization are likely to dominate next-generation refrigeration. Compact, energy-efficient models for urban dwellers combined with advanced organization accessories will cater to evolving lifestyles and environmental demands.
—
In summary, effective fridge organization combines understanding appliance zones, decluttering, labeling, specialized storage, and sustainability measures. These practical tips ensure fresher food, cost savings, and energy efficiency. By embracing evolving technologies and smart practices, future fridge management will become increasingly seamless and eco-friendly—redefining one of the most essential home appliances in our daily lives.