In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining a healthy diet can often feel like a daunting task. With busy schedules, work demands, and social commitments, many people resort to quick, processed meals that lack vital nutrients. This trend has heightened the importance of healthy meal prep lunches, which not only save time but also promote balanced nutrition. Meal prepping allows individuals to plan, portion, and prepare meals in advance, ensuring consistent intake of wholesome ingredients without compromising convenience.
Healthy meal prep lunches can transform your approach to eating by integrating fresh vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats into your diet. This method has been shown to improve dietary quality significantly. According to a study published in the journal *Appetite*, individuals who prepared meals ahead of time consumed fewer calories and more nutrients compared to those who did not plan meals in advance (Smith et al., 2017). Hence, meal prep is a practical solution that supports long-term health goals.
The Benefits of Healthy Meal Prep Lunches
One of the primary advantages of meal prepping is the ability to control portion sizes and nutrient intake. Overeating often occurs when meals are unplanned or eaten spontaneously. When meals are pre-portioned, it becomes easier to avoid overeating and ensure adequate calorie consumption tailored to individual needs. This control is especially beneficial for people aiming to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
Besides portion control, meal prepping encourages a diverse intake of nutrients. For example, incorporating a balance of macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in each meal is easier with thoughtful planning. Research from the American Heart Association highlights that balanced meals with appropriate macronutrient distribution improve heart health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases (AHA, 2021). Moreover, prepped meals tend to minimize the reliance on unhealthy snacks and fast food, which are often high in sodium and added sugars.
Key Components of Balanced Meal Prep Lunches
When preparing healthy lunches, it’s crucial to focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy and health benefits. Consider the following groups when designing your meal prep:
Proteins – Lean proteins like chicken breast, turkey, tofu, legumes, and fish such as salmon provide essential amino acids required for muscle repair and satiety.
Vegetables – Incorporating a colorful variety of vegetables like spinach, bell peppers, broccoli, and carrots increases fiber intake and delivers vitamins and antioxidants.
Whole Grains – Brown rice, quinoa, barley, and whole wheat pasta offer complex carbohydrates and fiber that aid digestion and maintain steady energy levels.
Healthy Fats – Sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil improve brain function and heart health.
For example, a standardized healthy meal prep lunch may consist of baked salmon, quinoa, steamed broccoli, and a side of sliced avocado. This combination provides omega-3 fatty acids, complex carbs, fiber, and monounsaturated fats essential for overall well-being.
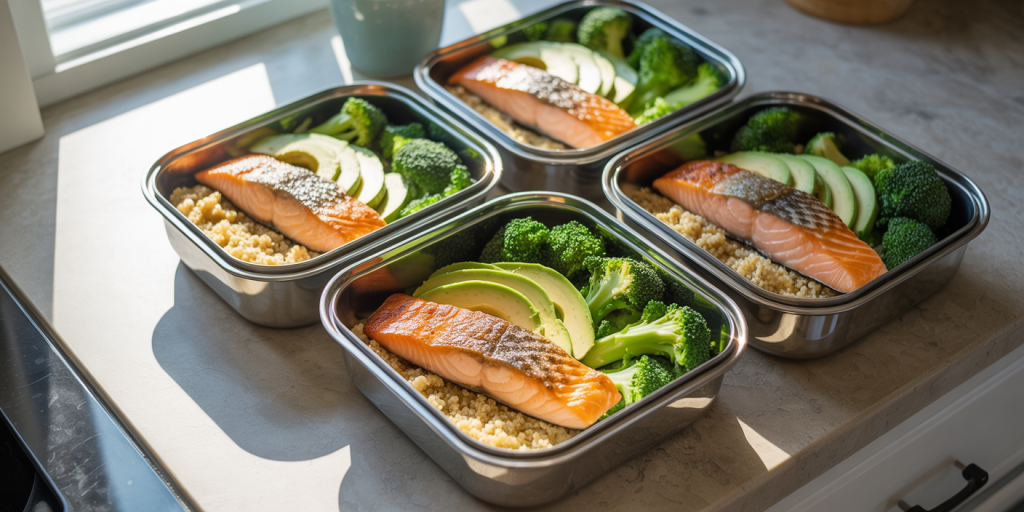

Comparative Table: Macronutrient Content of Typical Meal Prep Proteins
| Protein Source | Calories (per 100g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Carbohydrates (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken breast | 165 | 31 | 3.6 | 0 |
| Tofu | 76 | 8 | 4.8 | 1.9 |
| Salmon | 208 | 20 | 13 | 0 |
| Lentils | 116 | 9 | 0.4 | 20 |
This comparison illustrates that proteins such as chicken breast and salmon provide significant protein with minimal carbohydrates, suitable for people seeking low-carb diets, while lentils offer a good balance of protein and carbs for plant-based diets.
Planning and Preparing Meals: Practical Strategies
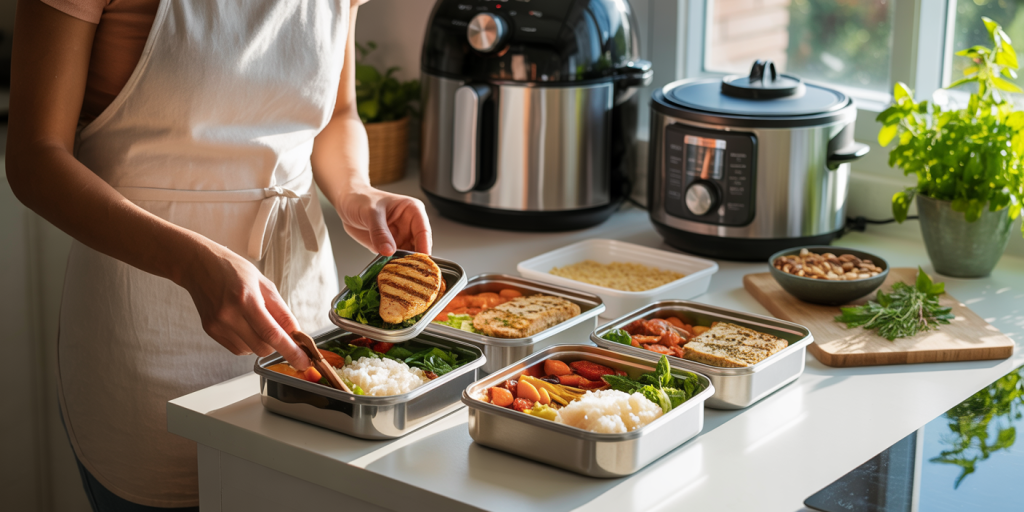
Successful healthy meal prep begins with careful planning. Start by creating a weekly menu that includes a variety of meals to prevent monotony. Batch cooking is a time-efficient method that involves preparing large quantities of ingredients or meals in advance to be stored and consumed later.
A practical example is roasting a mix of vegetables, cooking grains like brown rice or quinoa, and grilling proteins such as chicken breast or tofu over the weekend. These components can be stored separately in airtight containers and combined in different ways throughout the week.
Meal prep doesn’t have to be complicated or require a lot of time. Simple tools like slow cookers, instant pots, and air fryers facilitate quick cooking with minimal supervision. According to a survey conducted by the NPD Group in 2022, 68% of Americans reported using kitchen appliances to aid meal prep, indicating the growing popularity of these methods.

Nutritional Considerations for Special Diets
Meal prep lunches can be tailored to accommodate dietary restrictions and personal preferences such as vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, or keto diets. Each diet has unique nutritional requirements that can be met through thoughtful ingredient selection.
For vegetarians and vegans, protein sources include lentils, chickpeas, tempeh, and seitan, accompanied by whole grains and a variety of vegetables. Emphasizing iron-rich foods and vitamin B12-fortified products is vital to prevent nutrient deficiencies. Using fortified nutritional yeast or supplements can support those following strict plant-based diets.
For gluten-free meal preppers, whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and millet are excellent carbohydrate sources, as they naturally lack gluten. It’s essential to verify that all processed ingredients are certified gluten-free to avoid cross-contamination.
Keto diet enthusiasts focus on low-carb, high-fat meals. Meal prep lunches might feature options like spinach salad with grilled chicken, avocado, cheese, and olive oil dressing. Attention is required to balance fat intake while maintaining nutrient diversity.
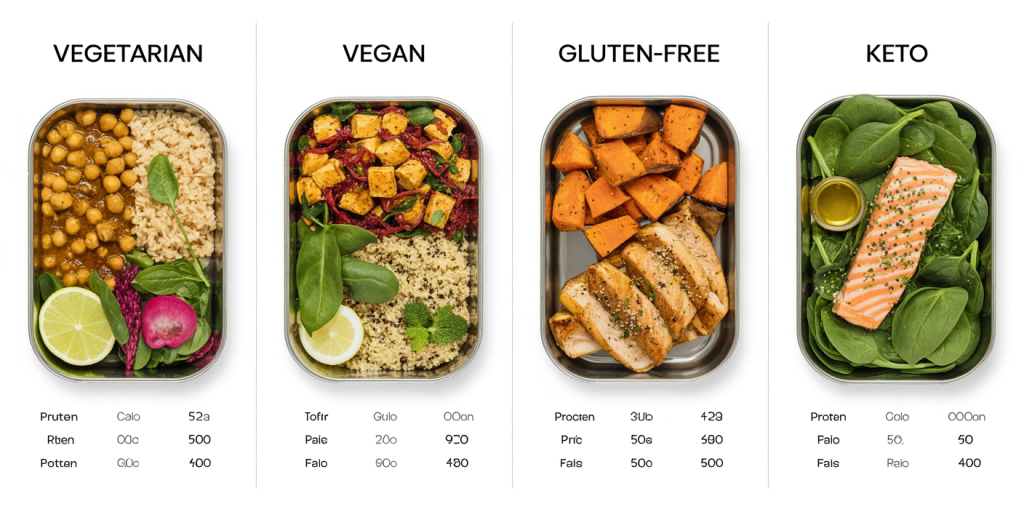
Comparative Table: Sample Meal Prep Lunches for Different Diets
| Diet Type | Example Meal | Primary Protein | Carbohydrate Source | Fat Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetarian | Chickpea and vegetable curry with rice | Chickpeas | Brown rice | Coconut milk |
| Vegan | Tofu stir-fry with quinoa and veggies | Tofu | Quinoa | Sesame oil |
| Gluten-Free | Grilled chicken with roasted sweet potato | Chicken breast | Sweet potato | Avocado |
| Keto | Spinach salad with salmon and olive oil | Salmon | Leafy greens (minimal carbs) | Olive oil, avocado |
This table helps visualize how meal preppers can customize lunches to comply with dietary guidelines while preserving nutritional adequacy.
Real-Life Success Stories: The Impact of Meal Prepping
Consider the case of Rachel, a 32-year-old marketing professional who struggled with midday energy slumps and unhealthy snacking. After adopting a healthy meal prep habit, she reported notable improvements in energy levels and weight management. Rachel found that dedicating two hours on Sundays to prepare balanced lunches allowed her to avoid fast food and control her calorie intake consistently. Her BMI decreased from 27 to 23 in six months, and she experienced reduced cravings for sugary snacks.
Another example is Marcus, a university student managing a gluten intolerance. By meal prepping lunches comprising grilled chicken, quinoa, and assorted vegetables, he was able to maintain a nutritious diet despite limited dining options on campus. Marcus reported improved focus and digestive health, attributing these benefits to his meal prepping routine.
These anecdotes underscore the transformative potential of meal prep in shaping healthier lifestyles.
Storage and Safety Tips for Meal Prep Lunches
Proper storage is critical to ensure food safety and preserve nutritional quality. Refrigerate prepped meals promptly and consume them within 3-4 days to avoid bacterial growth. Use airtight containers made of glass or BPA-free plastic to extend shelf life and prevent contamination.
Labeling containers with preparation dates helps monitor freshness. For meals prepared in larger quantities, consider freezing portions and thawing them daily to maintain optimal flavor and safety. The USDA recommends reheating food to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to eliminate potential pathogens.
Meal prep hygiene also involves handling raw meats separately from vegetables and thoroughly washing produce to minimize risks of foodborne illnesses.
Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives in Healthy Meal Prepping
The future of healthy meal prep lunches is intertwined with technological advancements, sustainability, and personalized nutrition. Mobile apps and AI-driven platforms are increasingly enabling users to customize meal plans based on their health goals, dietary restrictions, and biometric data. Companies like Mealime and Yummly offer tailored meal prep recipes optimized for nutritional balance and convenience.
Sustainability concerns are prompting meal prep enthusiasts to prioritize local, organic, and seasonal ingredients, reducing environmental impact. Meal kits and pre-portioned ingredients from eco-conscious brands may shape consumer preferences in the coming years.
Furthermore, nutrigenomics—a field studying the interaction between nutrition and genes—is likely to influence how personalized meal preps are designed, catering to individual metabolic responses and optimizing health outcomes.
Integration of smart kitchen devices capable of automated cooking and portioning is also on the horizon, potentially revolutionizing the efficiency and appeal of meal prepping.
—
Healthy meal prep lunches represent a practical, effective pathway to achieve balanced nutrition and manage lifestyle demands. By understanding essential nutrient components, employing strategic planning, and embracing emerging trends, individuals can optimize their diet for improved health and convenience. As more people adopt meal prepping, the combined benefits for personal health and the environment continue to grow, paving the way for a more nutritious, sustainable future.
—
References: Smith, L., et al. (2017). Impact of meal planning and preparation on diet quality and energy intake. *Appetite*, 123, 112-118. American Heart Association (2021). Balanced Diet for Heart Health. Retrieved from [heart.org](https://www.heart.org) NPD Group (2022). Survey on Home Kitchen Appliance Use. Market Research Report. USDA Food Safety Guidelines. (2023). Safe food handling.

Deixe um comentário