The concept of Meatless Monday has grown steadily in popularity, encouraging individuals and families to reduce their meat consumption one day a week. The practice aims to improve health, reduce environmental impact, and promote animal welfare without demanding a full commitment to vegetarianism or veganism. However, many people—especially devoted carnivores—struggle with the idea of earning satisfaction from a meal without meat on the plate. This article explores a detailed approach to crafting Meatless Monday dinners that not only appeal to vegetarians but also satisfy the cravings of even the most committed meat eaters.
The Growing Momentum of Meatless Mondays
Meatless Monday is more than just a trendy hashtag hashtag; it is backed by meaningful statistics and benefits. Studies by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health suggest that switching to one meatless day per week could reduce an individual’s carbon footprint by approximately 15%, a significant contribution toward global climate change mitigation. Health-wise, the American Heart Association reports that meals rich in plant-based foods and lower in saturated animal fats can lead to reduced risks of cardiovascular disease.
Despite these advantages, meat-centric traditions and preferences remain strong. Surveys report that nearly 90% of Americans still consume meat regularly, making it challenging to convince individuals to try meals without it. Therefore, crafting meatless recipes that replicate or reinvent textures, flavors, and nutritional benefits of meat is essential to broaden the appeal.
Incorporating Meat Substitutes That Deliver Flavor and Texture
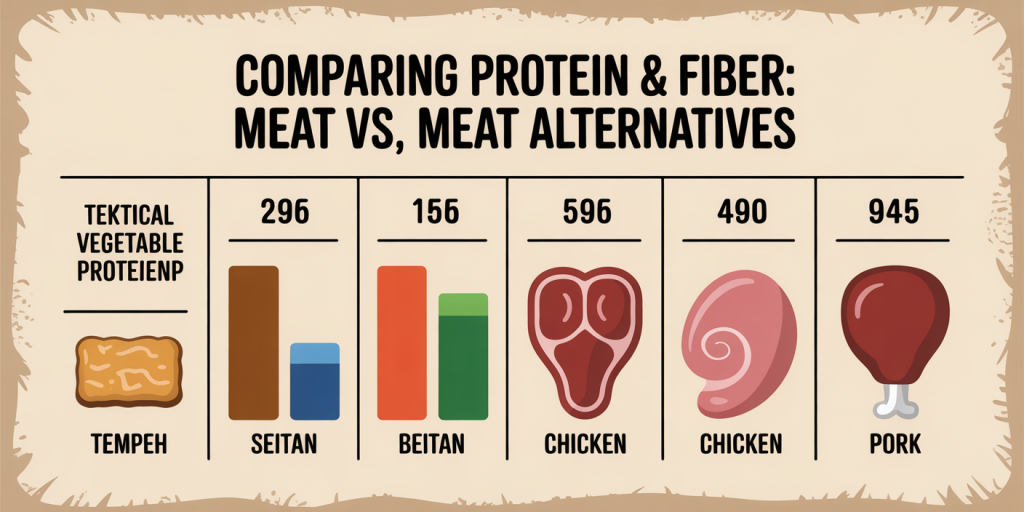
One of the most effective ways to make Meatless Monday dinners attractive to meat lovers is the smart use of meat substitutes. Products like tempeh, seitan, and textured vegetable protein (TVP) have been developed to imitate the chewiness and umami flavor that many crave from meat. Tempeh, a fermented soy product, offers a firm texture and a nutty taste that holds marinades well. Seitan, made from wheat gluten, provides a dense and chewy profile that can be spiced and cooked similarly to steak or chicken.
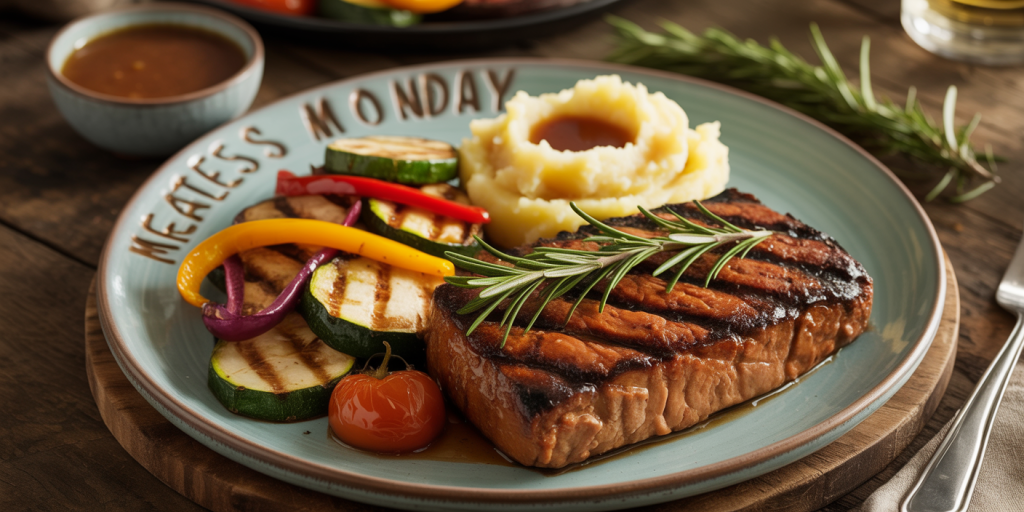
Take, for example, a recipe from chef Matthew Kenney, who specializes in plant-based dining. His smoked seitan steak, flavored with smoked paprika and garlic, can be grilled and sliced just like traditional beef steak. When served alongside roasted vegetables or creamy mashed potatoes, even meat lovers find satisfaction in the meal. Nutritionally, these substitutes supply an excellent source of protein and fiber. A 3-ounce serving of tempeh contains approximately 18 grams of protein and boasts higher fiber content than the same amount of beef, which contains zero fiber but about 22 grams of protein.

| Meat Substitute | Protein (per 3 oz) | Fiber (per 3 oz) | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tempeh | 18 g | 5 g | Stir-fries, sandwiches, grilling |
| Seitan | 21 g | 1 g | Stir-fries, steaks, sandwiches |
| Textured Soy Protein | 13 g | 3 g | Chilis, tacos, pasta sauces |
The chart highlights how these substitutes provide compelling nutrition alongside similar culinary applications. The key is seasoning and preparation techniques that build robust umami flavors.
Elevating Traditional Vegetarian Dishes for Meat Lovers
Another successful strategy is to enhance classic vegetarian recipes with bold flavors and textures. For example, dishes like lentil shepherd’s pie, stuffed bell peppers with quinoa and mushrooms, or creamy butternut squash risotto can be modified to satisfy fuller palates.
Lentil shepherd’s pie uses plant-based protein sources like lentils and mushrooms to replicate the hearty quality of traditional ground meat. Mushrooms, especially varieties like shiitake or portobello, have inherent umami flavors similar to beef. Adding smoked paprika, soy sauce, or miso paste can further deepen flavor profiles. When topped with creamy mashed potatoes, the dish becomes exceptionally comforting and filling.
A case study from a 2019 survey by the Vegetarian Resource Group found that dishes combining plant proteins and umami-rich vegetables led to higher satisfaction among meat eaters trying vegetarian meals for the first time. Interviewees frequently mentioned that texture and “meaty” flavor captured their interest more than simply replacing meat with rice or beans alone.
Leveraging Global Cuisines and Techniques
Global culinary traditions offer a treasure trove of flavorful vegetarian dishes that naturally focus on plants but appeal broadly. Take Indian cuisine, for example, which offers rich, spiced legume curries such as chana masala or dal makhani. These dishes use combinations of spices, slow cooking, and legumes that create dense, protein-rich meals with deep flavors. Many Indian families have been practicing meatless days culturally or for religious reasons, demonstrating the feasibility of fulfilling vegetarian meals through taste.

Similarly, Mediterranean diets emphasize vegetables, grains, legumes, and olive oil, often incorporating preparations like stuffed eggplants, chickpea stews, or falafel wraps. The use of herbs like oregano, basil, and thyme combined with tangy elements such as lemon juice or preserved lemons enhances flavor complexity.
By borrowing techniques such as slow roasting, marinating, and seasoning from international cuisines, cooks can craft meatless dishes that intrigue and satisfy even skeptical eaters.
Health and Environmental Benefits Quantified
The health benefits of meatless meals are well-documented. According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, diets rich in plant-based foods contribute to lower blood pressure, reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and decreased incidence of certain cancers. A comparative study published in *The Journal of Nutrition* found that participants who incorporated even one meatless day per week saw improvements in cholesterol levels and body mass index over a six-month period.
From an environmental perspective, the production of red meat accounts for about 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, as stated by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Replacing beef with beans, lentils, or plant-based meat alternatives for just one day per week could save approximately 100 gallons of water and reduce greenhouse gases by up to 7 pounds per meal.
| Impact Area | Meat-Based Meal (Typical Beef) | Meatless Alternative | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | 27 kg CO2 eq | 5 kg CO2 eq (lentils/beans-based) | -81% |
| Water Usage (per meal) | 450 gallons | 25 gallons (vegetable-based) | -94% |
| Land Use | 1000 sq ft | 100 sq ft (plant crops) | -90% |
Such clear metrics illustrate that Meatless Monday can act as a meaningful step toward sustainability, making the practice appealing not only for personal health but planetary well-being.
Future Perspectives: A Shift Toward Plant-Forward Diets
Looking ahead, the trend toward Meatless Monday and plant-forward diets is expected to accelerate, fueled by increasing awareness of climate change, health concerns, and advances in food technology. Market research forecasts predict that the global plant-based meat market will reach a valuation exceeding $35 billion by 2027, growing at an annual rate above 15%. Innovations such as cultured meat and improved meat analogue products are likely to provide even more meat-like experiences for consumers.
Educational campaigns and partnerships with restaurants that feature meatless options can further normalize plant-based eating, transitioning Meatless Monday from a niche lifestyle choice to a mainstream habit. Governments and institutions worldwide are also beginning to encourage reduced meat consumption as part of dietary guidelines.
In practical terms, this future points to an expansion in the quality and variety of meatless meals suitable for a broader audience. Chefs and home cooks alike will benefit from new ingredients, recipes, and culinary technologies aimed at satisfying diverse tastes while maintaining the health and environmental advantages of plant-based eating.

Deixe um comentário